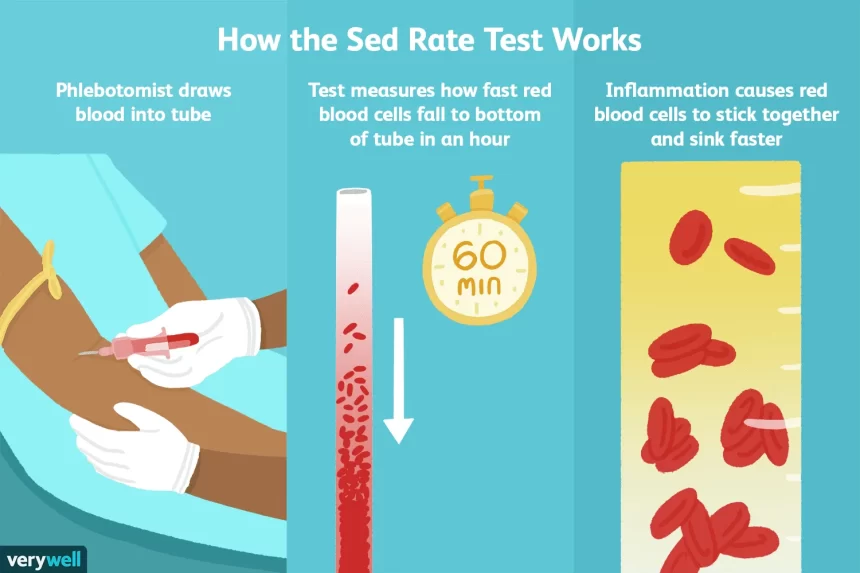
The Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) is a commonly used blood test that measures the rate at which red blood cells settle in a vertical tube over a specific period. It is a non-specific indicator of inflammation in the body and is often used as a diagnostic tool to monitor various health conditions.
While a high ESR can indicate an underlying health issue, it is essential to address the root cause and start following steps on how to reduce ESR. In this article, we will explore the definition of ESR, symptoms of high ESR, and practical ways to lower it.
Understanding ESR:
ESR measures the inflammatory response in the body. During inflammation, certain proteins in the blood, known as acute-phase reactants, increase, causing the red blood cells to clump together and settle more rapidly.
The ESR is a measurement of how quickly they settle. The test involves drawing a blood sample and monitoring the rate of sedimentation over an hour.
Symptoms of High ESR:
A high ESR does not cause specific symptoms on its own. However, it is often associated with underlying conditions that may present various symptoms. Some common symptoms of high ESR include the following:
- Weakness and Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and a general feeling of weakness can be symptoms of an underlying health issue associated with a high ESR.
- Fever: Inflammatory conditions often lead to an elevated body temperature, resulting in a fever.
- Joint Pain and Stiffness: Inflammation in the joints can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus are associated with high ESR and joint symptoms.
- Muscle Aches: An elevated ESR can be a sign of muscle inflammation, leading to muscle aches and discomfort.
- Unexpected Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss can be a symptom of certain conditions associated with a high ESR, such as cancer or chronic infections.
- General Malaise: Overall feelings of discomfort, malaise, or unwellness can be associated with elevated ESR levels.
How to Reduce ESR?
While it is important to address the underlying cause of a high ESR, and if you are wondering how to reduce ESR then here are some practical approaches:
- Treat Underlying Conditions: Identifying and treating the underlying condition causing the elevated ESR is crucial.
- Follow an Anti-inflammatory Diet: Adhering to an anti-inflammatory diet can help reduce inflammation in the body, potentially lowering ESR levels. Emphasize whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, healthy fats, and lean proteins. Limit or avoid inflammatory foods like refined sugars, processed foods, and saturated fats.
- Engage in Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity has been shown to reduce inflammation in the body. Incorporate exercises you enjoy, such as walking, jogging, swimming, or yoga, into your routine.
- Ensure Adequate Sleep: Getting enough quality sleep is vital for overall health and helps regulate inflammation in the body. Sleep for 7-9 hours each night, undisturbed.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for reducing inflammation. If overweight or obese, strive for gradual and sustainable weight loss through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Consider Herbal Supplements and Anti-inflammatory Foods: Certain herbal supplements, such as turmeric, ginger, and omega-3 fatty acids, possess anti-inflammatory properties. Incorporating these supplements or including foods rich in these compounds in your diet may help reduce inflammation and ESR levels.
It is important to note that reducing ESR requires a holistic approach and individualized care. Consult with a healthcare professional to identify the underlying cause of elevated ESR and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Conclusion:
ESR is an indicator of inflammation in the body and is often associated with underlying health conditions. While a high ESR does not cause specific symptoms, it is important to address the root cause and take steps to lower it.
By treating underlying conditions, adopting an anti-inflammatory lifestyle, and implementing strategies like regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep, it is possible to reduce ESR levels and promote overall well-being. Always consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance in managing ESR and associated health concerns.