The global pact towards a cleaner, more sustainable environment is accelerating, largely propelled by an expanding shift from conventional energy sources to renewable energy. This shift is becoming ever more crucial as the effects of climate change become strikingly apparent. As societies globally wrestle with the challenge of reducing their carbon footprint, renewable energy has emerged as a pivotal force guiding us toward a more sustainable Earth.
Bucking the misconception fostered by certain narratives, such as the one portrayed in Michael Moore’s documentary, Planet of the Humans, renewable energy technologies are not just feasible, but are evolving at a rapid pace. Over the past decade, the cost of renewable energy has significantly declined, its efficiency has advanced, and solutions for incorporating these resources into our electrical grids have markedly improved.
Primarily, renewable energy sources, notably wind and solar power, are successfully replacing fossil fuel energy on the grid. This is true for virtually every region, including the United States, where wind or solar energy, when available, supersedes energy produced by natural gas or coal-fired generators. According to several studies, including one by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, increasing our dependence on wind and solar energy could lead to a considerable reduction in CO2 emissions. This shift is already noticeable, with wind and solar farms steadily replacing traditional power plant constructions. Furthermore, companies are providing technology that offers increased flexibility and control over energy consumption, like off grid solar systems.
The transformative power of renewable energy:
The transformative power of renewable energy goes beyond environmental preservation. It also represents an emerging dynamo in job creation. In the United States, the clean energy sector employed roughly 3.4 million workers at the outset of 2020. Moreover, these jobs usually offer higher wages, making the sector a driving force of both environmental sustainability and socioeconomic progress.
As we plot our journey towards a more sustainable Earth, we must also recognize the advancements made in mitigating the environmental impact of renewable energy infrastructure. Both wind and solar plants are built with minimal environmental impact, often yielding additional benefits. Wind farms, for instance, can offer annual revenues for farmers and ranchers, while simultaneously contributing to county property taxes that bolster local community services.
A significant milestone in our transition towards renewable energy dominance is the plummeting cost of solar and wind power. According to Bloomberg New Energy Finance, the global cost of onshore wind and utility-scale solar has dramatically dropped in the past decade. This trend has considerably enhanced the competitiveness of renewable energy.
The inherent variability in the production of wind and solar energy presents a challenge. However, we’ve seen utilities and grid operators efficiently manage this through forecasting, responsive loads, and infrastructural modifications, such as storage and transmission.
Energy storage:
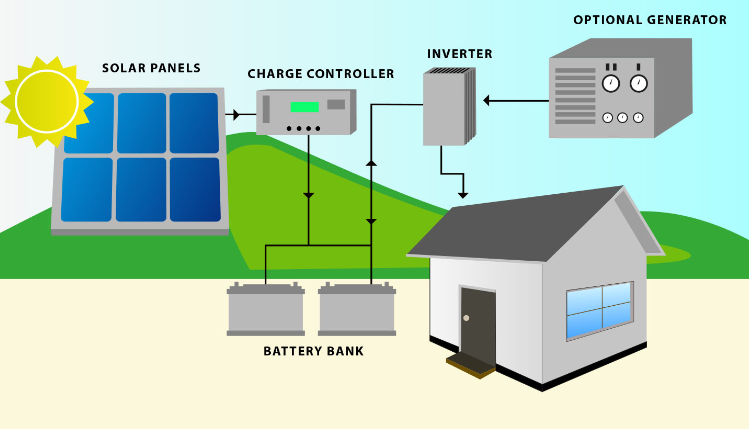
Energy storage, particularly battery storage, has emerged as a promising solution to the variability of wind and solar power. Battery energy storage, predominantly in the form of Lithium-ion batteries, is experiencing rapid growth due to its declining costs. These batteries act as efficient reservoirs of energy and, when charged by renewable sources, contribute no additional greenhouse gas emissions.
Renewable energy facilities:
Renewable energy facilities have proven to be enduring investments. The average operational lifespan of wind turbines is estimated to be about 20 years, while photovoltaic systems can remain functional for 25 to 40 years. The implementation of more efficient technologies may even allow for earlier equipment turnover, significantly boosting electricity production at existing sites.
Sceptics often question whether renewable energy sources generate more energy than they consume. Numerous studies have shown that renewable energy sources significantly outperform fossil fuel-fired power plants in this regard. Moreover, while the manufacture of solar panels requires substantial amounts of energy, they typically offset this consumption within two years of operation.
Lastly, the electrification of transport, especially through electric vehicles (EVs), has gained significant momentum in the drive towards reduced emissions. EVs are not only more efficient than conventional vehicles but also have zero tailpipe emissions. However, an EV’s net carbon footprint does depend on the electricity used to charge it.
Key Takeaways
- Renewable energy is crucial for a sustainable future, as it reduces carbon emissions and creates jobs.
- Wind and solar power are replacing fossil fuels on the grid, leading to lower CO2 emissions.
- Advances in technology have made renewable energy more efficient and cost-effective.
- Energy storage, such as battery storage, helps manage the variability of renewable energy sources.
- Renewable energy infrastructure has minimal environmental impact and offers additional benefits to local communities.
- The electrification of transport, especially through electric vehicles, contributes to reduced emissions.
- Overall, renewable energy is a transformative force driving us towards a cleaner and more sustainable Earth.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, as we collectively strive towards a more sustainable Earth, the role of renewable energy cannot be underestimated. It is a driving force that is not only altering our energy consumption patterns but also influencing socioeconomic development and job creation. Misconceptions and outdated information should not detract from the reality: renewable energy is here, it’s progressing, and it’s pivotal for our sustainable future.